链表
本文为学习代码随想录时所做的笔记,仅供学习参考,不做任何商业用途,若有侵权,请联系删除。
链表的定义
1 | |
可以不定义构造函数,C++默认生成一个构造函数,但是这个构造函数不会初始化任何成员变量
自定义的构造函数初始化节点
- ```c++ ListNode* head = new ListNode(5) ;
1
2
3
4
5
6
- 使用默认构造函数初始化节点
- ```c++
ListNode* head = new ListNode();
head->val = 5;
- ```c++ ListNode* head = new ListNode(5) ;
移除链表元素
直接使用原来的链表进行移除节点操作
```c++ class Solution { public: ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) { // 删除头结点 while (head != NULL && head->val == val) { // 注意这里不是if ListNode* tmp = head; head = head->next; delete tmp; }
// 删除非头结点 ListNode* cur = head; while (cur != NULL && cur->next!= NULL) { if (cur->next->val == val) { ListNode* tmp = cur->next; cur->next = cur->next->next; delete tmp; } else { cur = cur->next; } } return head; }};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
- 设置一个虚拟头结点
- ```c++
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0); // 设置一个虚拟头结点
dummyHead->next = head; // 将虚拟头结点指向head,这样方面后面做删除操作
ListNode* cur = dummyHead;
while (cur->next != NULL) {
if(cur->next->val == val) {
ListNode* tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
delete tmp;
} else {
cur = cur->next;
}
}
head = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return head;
}
};
设计链表
1 | |
反转链表
双指针法
- ```c++ class Solution { public: ListNode* reverseList(ListNode*
head) { ListNode* temp; // 保存cur的下一个节点 ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* pre = NULL; while(cur) { temp = cur->next; // 保存一下
cur的下一个节点,因为接下来要改变cur->next cur->next = pre; //
翻转操作 // 更新pre 和 cur指针 pre = cur; cur = temp; } return pre; } };
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
- 递归
- ```c++
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* pre,ListNode* cur){
if(cur == NULL) return pre;
ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
// 可以和双指针法的代码进行对比,如下递归的写法,其实就是做了这两步
// pre = cur;
// cur = temp;
return reverse(cur,temp);
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
// 和双指针法初始化是一样的逻辑
// ListNode* cur = head;
// ListNode* pre = NULL;
return reverse(NULL, head);
}
}
- ```c++ class Solution { public: ListNode* reverseList(ListNode*
head) { ListNode* temp; // 保存cur的下一个节点 ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* pre = NULL; while(cur) { temp = cur->next; // 保存一下
cur的下一个节点,因为接下来要改变cur->next cur->next = pre; //
翻转操作 // 更新pre 和 cur指针 pre = cur; cur = temp; } return pre; } };
两两交换链表中的节点
初始时
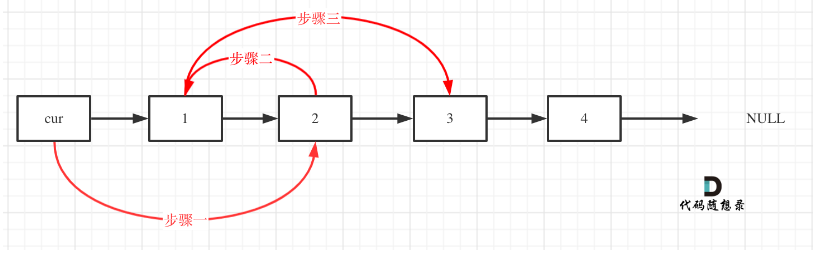
操作之后
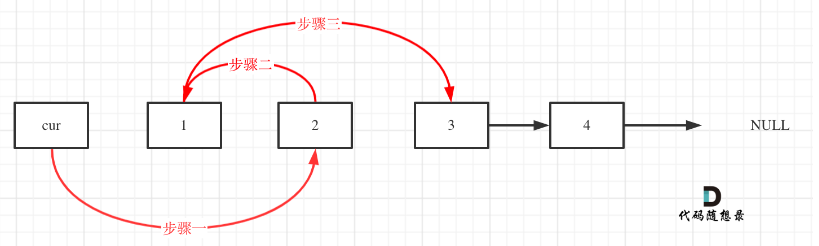
1 | |
删除链表的倒数第N个节点
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 | |
链表相交
面试题 02.07. 链表相交 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 | |
环形链表
判断链表是否有环
使用快慢指针法,分别定义fast和slow指针,从头结点出发,fast指针每次移动两个节点,slow指针每次移动一个节点,如果 fast 和 slow指针在途中相遇 ,说明这个链表有环。
fast指针一定先进入环中,如果fast指针和slow指针相遇的话,一定是在环中相遇
有环时两者一定会相遇

如果有环,如何找到这个环的入口
假设从头结点到环形入口节点 的节点数为x。 环形入口节点到 fast指针与slow指针相遇节点 节点数为y。 从相遇节点 再到环形入口节点节点数为 z。
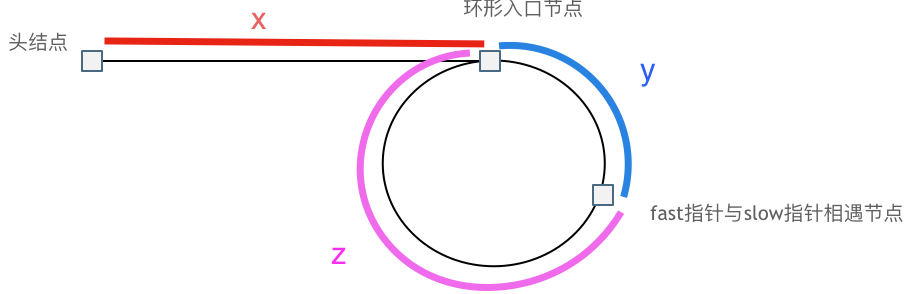
- slow指针走过的节点数:
x+y - fast指针走过的节点数:
x+y+n(y+z),n为fast走过的圈数 - slow * 2 == fast,即可以得到
x+y = n(y+z),可得x = n (y + z) - y - 当
n = 1时

- 当
n > 1的情况与n = 1类似,只是fast指针环中转了n圈
slow的步数是x+y而不是x + 若干环的长度 + y
首先slow进环的时候,fast一定是先进环来了。
如果slow进环入口,fast也在环入口,那么把这个环展开成直线,就是如下图的样子
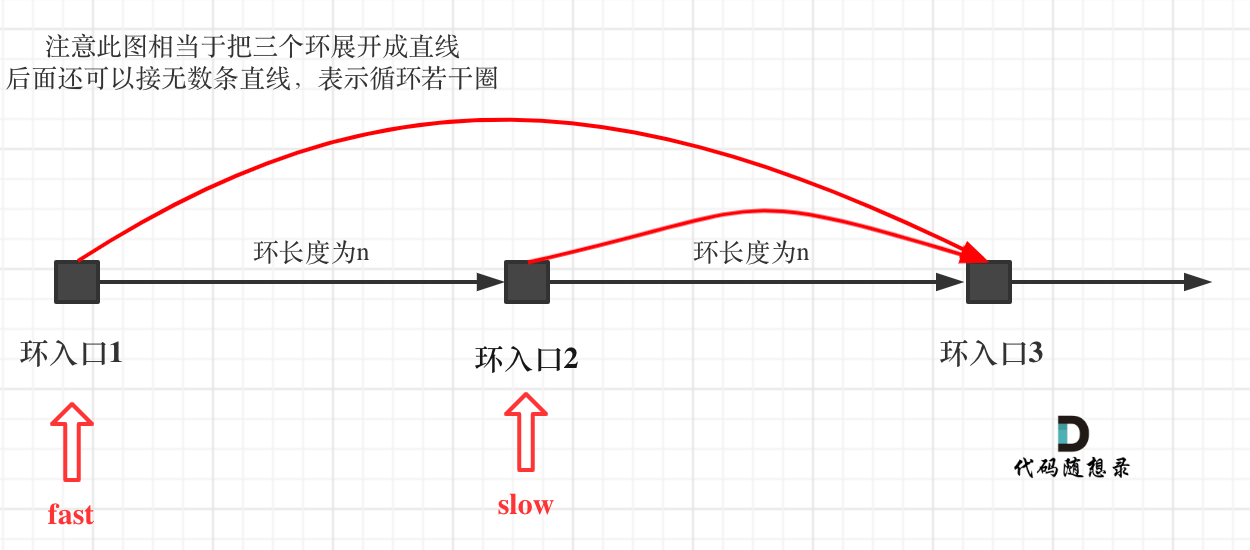
可以看出如果slow 和 fast同时在环入口开始走,一定会在环入口3相遇,slow走了一圈,fast走了两圈。
重点来了,slow进环的时候,fast一定是在环的任意一个位置,如图:
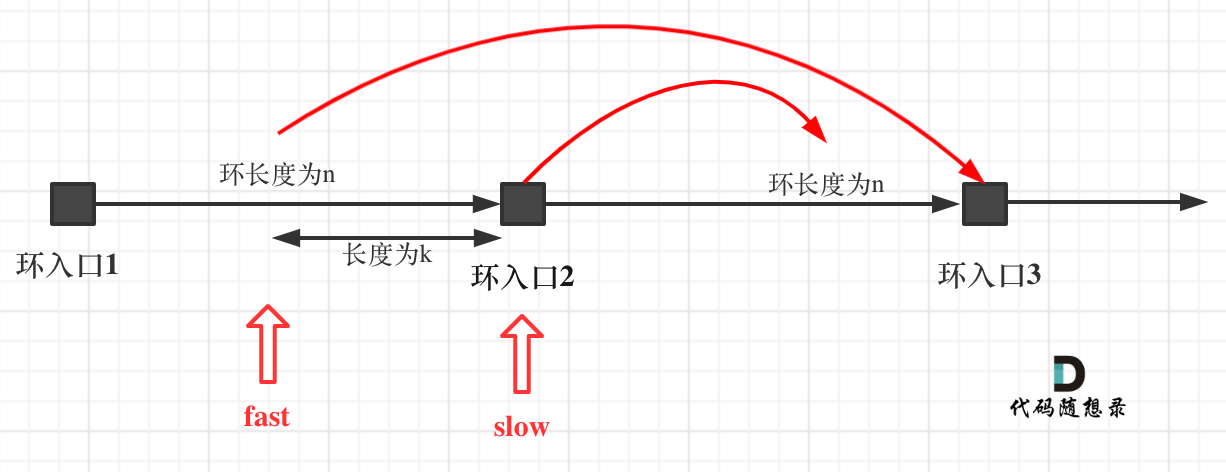
那么fast指针走到环入口3的时候,已经走了k + n 个节点,slow相应的应该走了(k + n) / 2 个节点。
因为k是小于n的(图中可以看出),所以(k + n) / 2 一定小于n。
也就是说slow一定没有走到环入口3,而fast已经到环入口3了。
这说明什么呢?
在slow开始走的那一环已经和fast相遇了。
假设Faster确实把Slower超了而且他俩还没相遇(类似Faster一下迈了2步,Slower一下迈了一步,Faster超了Slower,但是俩人并没遇上)。那么就假设Faster现在在 i+1 位置而Slower在 i 位置。那么前一时刻,Slower肯定是在 i-1 位置,而Faster肯定在(i+1)-2位置,所以前一时刻,俩人都在 i-1 位置,相遇了。
1 | |